QUINUA CONSUMPTION BENEFITS
Quinoa – Nutritional value
The consumption of quinoa is increasingly popular among people interested in improving and maintaining their health status by changing dietary habits since it is an excellent example of “functional food” (which helps to reduce the risk of various diseases exercising health promotion). This food, for its superior nutritional characteristics, can be very useful in the stages of development and growth of the organism. In addition, it is easy to digest, contains no cholesterol and lends itself to the preparation of complete and balanced diets.
Quinoa can also be used in both common diets and vegetarian diets, as well as special diets for certain consumers such as older adults, children, high performance athletes, diabetics, celiac and lactose intolerant people.
Proteins
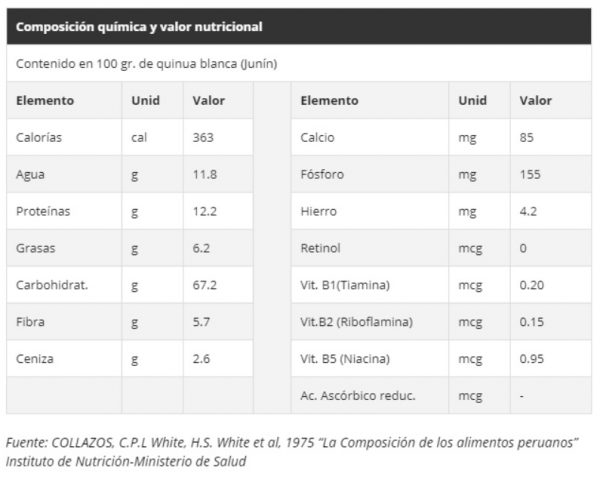
Quinoa is characterized by its high protein value, where the quality of its proteins and balance are higher in this one than in the other cereals, fluctuating between 12.5 to 16.7%. 37% of the proteins that quinoa has are made up of essential amino acids.
The essential amino acids are those that are not produced by the body, so they need to be ingested through the diet. The lack of these amino acids in the diet limits the development of the organism, since it is not possible to replenish the cells of the dying tissues or create new tissues, in the case of growth. For the human being, the essential amino acids are: Valine, Leucine, Threonine, Lysine, Tryptophan, Histidine, Phenylalanine, Isoleucine, Arginine and Methionine.
Fat
Most of the fats in quinoa are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated. These are beneficial for the body when they are incorporated into the diet, since they are elementary in the formation of the structure and in the functionality of the nervous and visual system of the human being. Its consumption, in turn, decreases the level of total cholesterol and LDL (bad cholesterol) in the blood – just to name a few of the many benefits that consumption of omega fatty acids has for the body. The values of fatty acids in the raw grain are 8.1%, 52.3%, 23% omega 3, omega 6 and omega 9, respectively.
Fiber
Quinoa is a food rich in fiber that varies its composition depending on the type of grain, with ranges ranging from 2.49 and 5.31g / 100 gr of dry matter. It has been shown that dietary fiber decreases the levels of total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, blood pressure and acts as an antioxidant. Antioxidants protect us against free radicals, which cause aging processes and some other diseases.
Gluten free
Quinoa is considered gluten-free because it contains less than 20mg / kg according to the Codex Alimentarius, which is useful for gluten allergy sufferers. The periodic consumption of quinoa helps the celiac to recover the normality of the intestinal villi, much more quickly than with the simple diet without gluten.
Minerals
The grain of quinoa has almost all minerals at a level higher than cereals. It contains phosphorus, calcium, iron, potassium, magnesium, manganese, zinc, lithium and copper. Its iron content is twice as high as that of wheat, three times higher than that of rice, and reaches almost to the level of beans.
It has 1.5 times more calcium compared to wheat. This is important, since calcium is responsible for several structural functions of bones and teeth, and participates in the regulation of neuromuscular transmission of chemical and electrical stimuli, cell secretion and blood coagulation. For this reason, calcium is an essential component of food. The recommended calcium intake in children aged 4 to 9 years is 600-700 / day and for adults it ranges from 1000 to 1300 mg / day (FAO / WHO, 2001).
Vitamins
Quinoa has a high content of vitamins of complex B, C and E, where its content of vitamin B and C is higher than that of wheat. It is rich in carotene and niacin (B3). It contains substantially more riboflavin (B2), tocopherol (vitamin E) and carotene than wheat and rice.